The History of Zero-Knowledge Proofs — And Why They Became Essential to Modern Cryptography
ZK is the future — and we’re only in the early chapters.
ZK is the future — and we’re only in the early chapters.
Over the last decade, zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) have gone from an obscure academic idea to one of the most important breakthroughs in cryptography and blockchain.
Today, ZK is powering everything from private transactions to scalable blockchains, verifiable computation, and next-generation trading systems like KalqiX.
But ZK didn’t appear suddenly.
Its journey spans 40 years, starting from a simple question:
“Can you prove something is true without revealing any information?”
This single question changed the future of digital privacy.
Let’s trace the history.
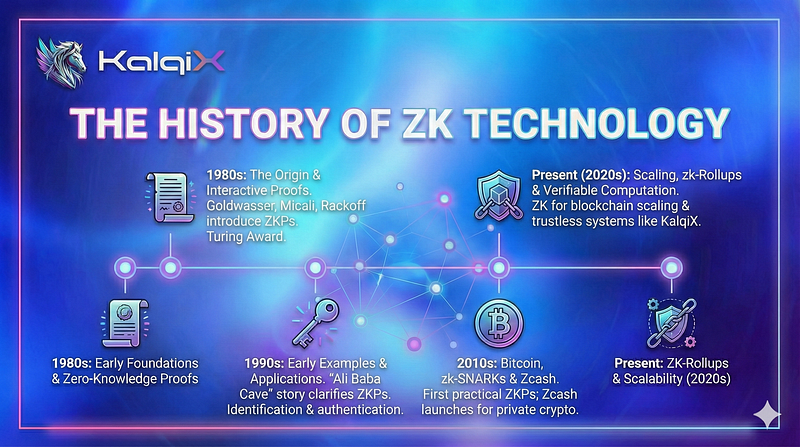
1. The Origin (1980s): When Three MIT Researchers Changed Cryptography Forever
1. The Origin (1980s): When Three MIT Researchers Changed Cryptography Forever
Zero-knowledge proofs were introduced in 1985 by three cryptographers:
• Shafi Goldwasser
• Silvio Micali
• Charles Rackoff
They published a groundbreaking paper:
“The Knowledge Complexity of Interactive Proof Systems”
This paper introduced the idea that:
• You can prove a statement is true
• Without revealing the statement itself
• And without sharing any additional information
This was a revolutionary idea.
At that time, cryptography was focused on:
• Encryption
• Authentication
• Signatures
But privacy of proofs was unexplored.
ZKPs opened a door to an entirely new world — where information could be verified without being exposed.
They also introduced the concept of interactive proofs:
the prover and verifier engage in a “conversation” where the prover convinces the verifier without revealing secrets.
This invention later won Goldwasser and Micali the Turing Award, the Nobel Prize of computing.
2. The Early Examples: Simple Stories That Explained a Hard Concept
Cryptographers introduced simple analogies so humans could understand ZKPs.
Most famously:
The Ali Baba Cave Story
(Jean-Jacques Quisquater, 1990)
A person can prove they know the secret password to open a magic door without telling you the password — simply by entering the cave and coming out through a path that requires the secret.
This showed the power of ZK:
• Proof without disclosure
• Verification without exposure
• Privacy without trust
This simple story helped the world understand the abstract mathematics behind ZK.
3. The First Real Applications (1990s–2000s)
In the 90s and early 2000s, ZK was mostly theoretical because:
• Proofs were too heavy
• Computation was slow
• Practical use cases were limited
• No one imagined digital currencies or blockchains yet
Still, ZK played an important role in:
• Identification without revealing passwords
• Authentication systems
• Privacy-preserving protocols in early security systems
But ZK was waiting for its perfect use case.
That use case arrived in 2009.
4. Bitcoin’s Arrival (2009): The Limitation That Sparked ZK Adoption
Bitcoin introduced public, transparent ledgers — everyone can see everything.
This transparency solved trust.
But it killed privacy.
You couldn’t prove something without exposing it.
And that’s where ZK became important again.
Researchers realized:
To scale blockchains AND protect privacy,
we need a way to verify transactions without revealing details.
Perfect job for zero-knowledge proofs.
5. zk-SNARKs & Zcash (2013–2016): The ZK Revolution Begins
In 2013, a team of researchers introduced the first practical zk-SNARKs:
• Short proofs
• Fast verification
• Non-interactive
• Efficient enough to run on blockchains
Three years later, in 2016, the Zcash project launched using zk-SNARKs to enable fully private transactions.
For the first time ever:
• A blockchain could verify transactions
• Confirm balances
• Enforce correctness
• Without revealing sender, receiver, or amount
This was a milestone.
Privacy in crypto became real, not theoretical.
6. Scaling Blockchains With ZK (2018–2022): The Era of zk-Rollups
As Ethereum became congested, teams realized:
ZK could also be used to compress and verify large batches of transactions.
This created zk-rollups — one of the biggest innovations in blockchain scaling.
Projects like:
• zkSync
• StarkNet
• Polygon zkEVM
• Scroll
…pushed ZK from privacy → scalability + verifiability.
Now ZK wasn’t just hiding information.
ZK was proving correctness of huge computations instantly.
This unlocked a new design space for decentralized apps.
7. Verifiable Computation & zkVMs (2022–Present): The Modern Breakthrough
Modern ZK is no longer just about hiding private data.
Today, ZK lets you:
• Prove that a program executed correctly
• Without showing the inputs
• And without running the program again
This is called verifiable computation.
zkVMs like:
• Risc Zero
• Succinct SP1
• Polygon Miden
• Jolt, Nova, Halo2
…allow developers to generate proofs for any computation.
This is the technology that powers next-gen systems like KalqiX, enabling:
• Verifiable matching
• Proof-based settlement
• Transparent fund flow
• High-performance trading
• Private intents
• Fraud-proof execution
ZK has become the backbone for trustless finance.
8. Why ZK Became Necessary
ZK wasn’t invented because it sounded cool.
It emerged to solve fundamental problems of the digital world.
Problem 1: Privacy
Banks, websites, governments — they all needed ways to authenticate without exposing sensitive data.
ZK solved it.
⸻
Problem 2: Trust
In systems run by centralized parties, users needed ways to verify correctness.
ZK solved it.
⸻
Problem 3: Scalability
Blockchains needed ways to validate huge amounts of computation quickly.
ZK solved it.
⸻
Problem 4: Fairness & Integrity
Apps, exchanges, and protocols needed a way to prove they weren’t cheating.
ZK solved it.
9. The Future: Zero-Knowledge Everywhere
Today, ZK is going mainstream.
It’s being used in:
• Trading systems (KalqiX)
• Supply chain audits
• Digital identity
• Gaming
• Payments
• Rollups
• AI verifiable computations
ZK is moving from a niche idea to the default foundation of trust in digital systems.
The future of blockchains, privacy, and verifiable computation will be powered by ZK.
Closing Thought
From a simple question in the 1980s to powering the most advanced systems today, zero-knowledge proofs have redefined how humans verify information.
Privacy, trust, and security no longer require compromise.
ZK is the future — and we’re only in the early chapters.
Follow us to know:
Website: www.kalqix.com
Testnet: testnet.kalqix.com
Twitter: https://x.com/kalqix
Telegram: https://t.me/kalqix
Discord: https://discord.com/invite/rmkkKvFDXv

